COMPUTATION OF INTEGRALS using a quadrature methods on a mesh. More...
Data Types | |
| interface | integ |
| Integration of scalar functions. More... | |
| interface | l2_dist |
| integral L2 distance More... | |
| interface | l2_dist_grad |
Functions/Subroutines | |
| real(rp) function | integ_scal_func (u, qdm) |
| Returns \( \int_O u(x) \dx \). More... | |
| real(rp) function | integ_scal_fe (E, u, uh, X_h, qdm) |
| Returns \( \int_O E(x, u(x), u_h(x)) \dx \). More... | |
| real(rp) function | integ_scal_fe_grad (E, phi, uh, X_h, qdm) |
| Returns \( \int_O E(x, \phi(x), \nabla u_h(x)) \dx \). More... | |
| real(rp) function, public | integ_scal_fe_grad_proj (E, phi, uh, X_h, qdm) |
| Returns \( \int_O E(x, \phi_T(x), \nabla u_h(x)) \dx \). More... | |
| real(rp) function | integ_scal_fe_grad_2 (E, uh1, uh2, X_h, qdm) |
| Returns \( \int_O E(x, \nabla u1_h(x), \nabla u2_h(x)) \dx \). More... | |
| real(rp) function | e_l2 (x, u1, u2) |
| \( (x-y)^2 \) More... | |
| real(rp) function | e_l2_vect (x, p1, p2) |
| \( (p-q)^2 \) More... | |
| real(rp) function | l2_dist_scalfe (u, uh, X_h, qdm) |
| Returns \( \int_O \vert u - u_h \vert^2 \dx \). More... | |
| real(rp) function | l2_dist_grad_scalfe (phi, uh, X_h, qdm) |
| Returns \( \int_O \vert \phi - \nabla u_h \vert^2 \dx \). More... | |
| real(rp) function, public | l2_dist_grad_proj (phi, uh, X_h, qdm) |
| Returns \( \int_O \vert \phi_T - \nabla u_h \vert^2 \dx \). More... | |
| real(rp) function, public | l2_dist_vect (phi, phi_h, X_h, qdm) |
| Returns \( \int_O \vert \phi - \phi_h \vert^2 \dx \). More... | |
Detailed Description
COMPUTATION OF INTEGRALS using a quadrature methods on a mesh.
Given:
- a mesh \( \mathcal{T} \) of a domain \( \Omega \),
- an integration method quadMesh on \( \mathcal{T}\),
This module proposes various computation of integrals with an integration domain composed of cells of the mesh \( \mathcal{T} \).
Integration domain: see quadmesh_mod mreamble for a definition.
Function/Subroutine Documentation
◆ e_l2()
|
private |
\( (x-y)^2 \)
Definition at line 875 of file integral.F90.
◆ e_l2_vect()
|
private |
\( (p-q)^2 \)
Definition at line 884 of file integral.F90.
◆ integ_scal_fe()
|
private |
Returns \( \int_O E(x, u(x), u_h(x)) \dx \).
- \( E~: \R^3 \times \R \times \R \mapsto \R \)
- \(u~: \R^3 \mapsto \R \) is a scalar function,
- \( u_h~: \Omega \mapsto \R\) is a scalar finite element function in the finite element space \( X_h \)
(associated to a mesh \( \T \) with domain \( \Omega \)),
- 'qdm' = integration method on the mesh \( \T \),
- \( O \) is the integration domain, see quadmesh_mod for a definition.
Definition at line 193 of file integral.F90.
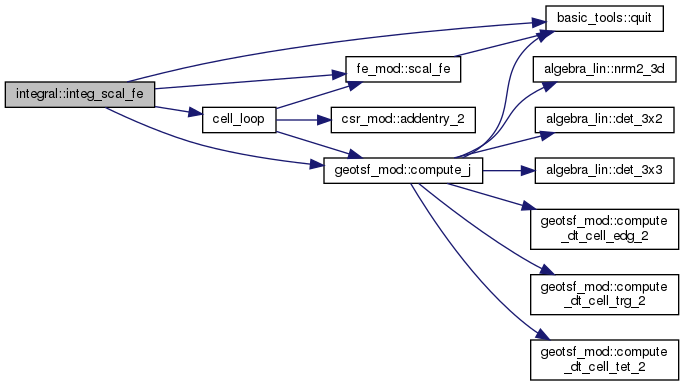
◆ integ_scal_fe_grad()
|
private |
Returns \( \int_O E(x, \phi(x), \nabla u_h(x)) \dx \).
- \( E~: \R^3 \times \R^3 \times \R^3 \mapsto \R \)
- \(\phi~: \R^3 \mapsto \R^3 \) is a vector function,
- \( u_h~: \Omega \mapsto \R\) is a scalar finite element function in the finite element space \( X_h \)
(associated to a mesh \( \T \) with domain \( \Omega \)),
- 'qdm' = integration method on the mesh \( \T \),
- \( O \) is the integration domain, see quadmesh_mod for a definition.
Definition at line 345 of file integral.F90.
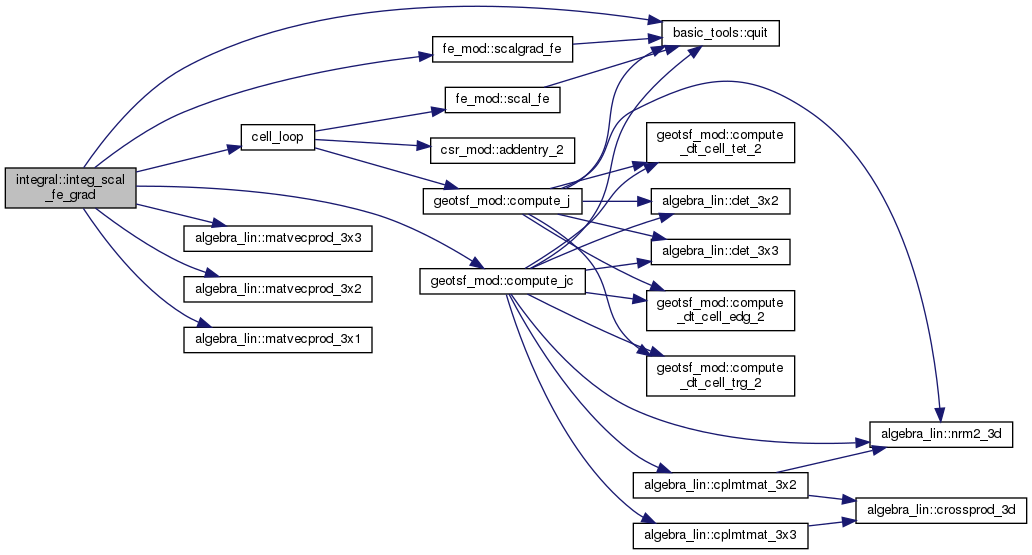
◆ integ_scal_fe_grad_2()
|
private |
Returns \( \int_O E(x, \nabla u1_h(x), \nabla u2_h(x)) \dx \).
- \( E~: \R^3 \times \R^3 \times \R^3 \mapsto \R \)
- \( ui_h~: \Omega \mapsto \R\) is a scalar finite element function in the finite element space \( X_h \)
(associated to a mesh \( \T \) with domain \( \Omega \)),
- 'qdm' = integration method on the mesh \( \T \),
- \( O \) is the integration domain, see quadmesh_mod for a definition.
Definition at line 702 of file integral.F90.
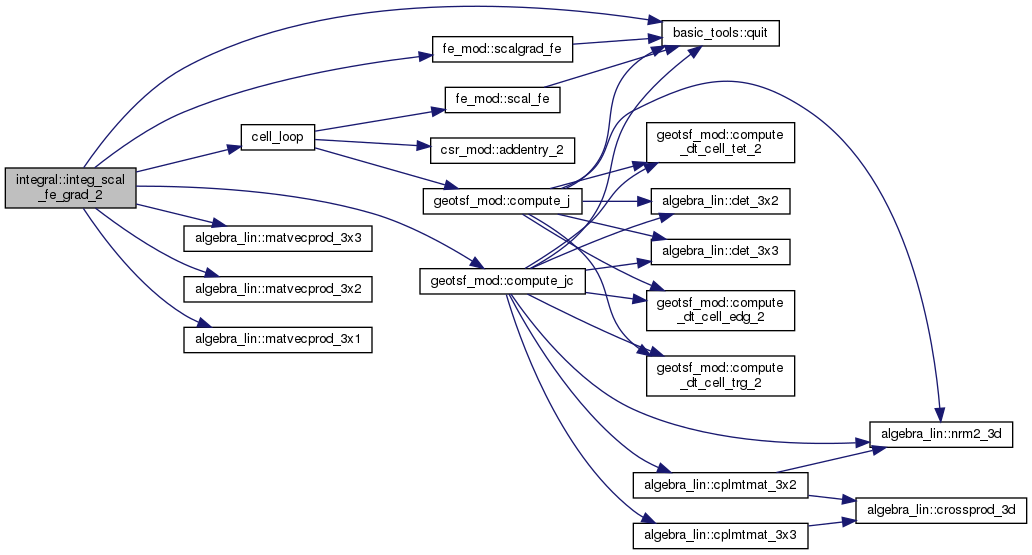
◆ integ_scal_fe_grad_proj()
| real(rp) function, public integral::integ_scal_fe_grad_proj | ( | procedure(r3xr3xr3tor) | E, |
| procedure(r3tor3) | phi, | ||
| real(rp), dimension(:), intent(in) | uh, | ||
| type(fespace), intent(in) | X_h, | ||
| type(quadmesh), intent(in) | qdm | ||
| ) |
Returns \( \int_O E(x, \phi_T(x), \nabla u_h(x)) \dx \).
same as integral::integ_scal_fe_grad BUT :
\( \phi_T \): tangent component of \( \phi\) in the tangent space to any cell in the integration domain O
Definition at line 511 of file integral.F90.
◆ integ_scal_func()
|
private |
Returns \( \int_O u(x) \dx \).
- \( u \) = scalar function,
- 'qdm' = integration method on a mesh,
\( O \) is the integration domain, see quadmesh_mod for a definition.
Definition at line 81 of file integral.F90.
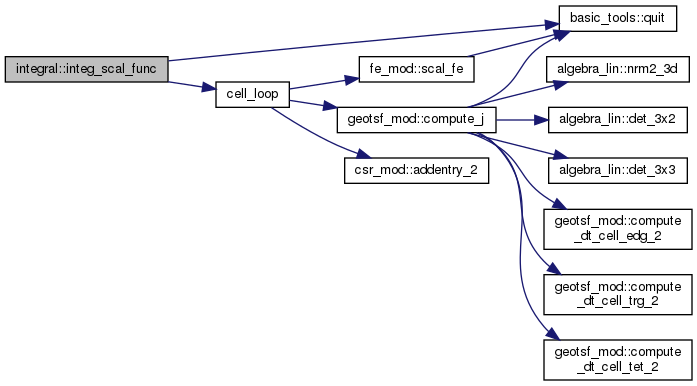
◆ l2_dist_grad_proj()
| real(rp) function, public integral::l2_dist_grad_proj | ( | procedure(r3tor3) | phi, |
| real(rp), dimension(:), intent(in) | uh, | ||
| type(fespace), intent(in) | X_h, | ||
| type(quadmesh), intent(in) | qdm | ||
| ) |
Returns \( \int_O \vert \phi_T - \nabla u_h \vert^2 \dx \).
same as integral::l2_dist_grad BUT :
\( \phi_T \): tangent component of \( \phi\) in the tangent space to any cell in the integration domain O
Definition at line 956 of file integral.F90.
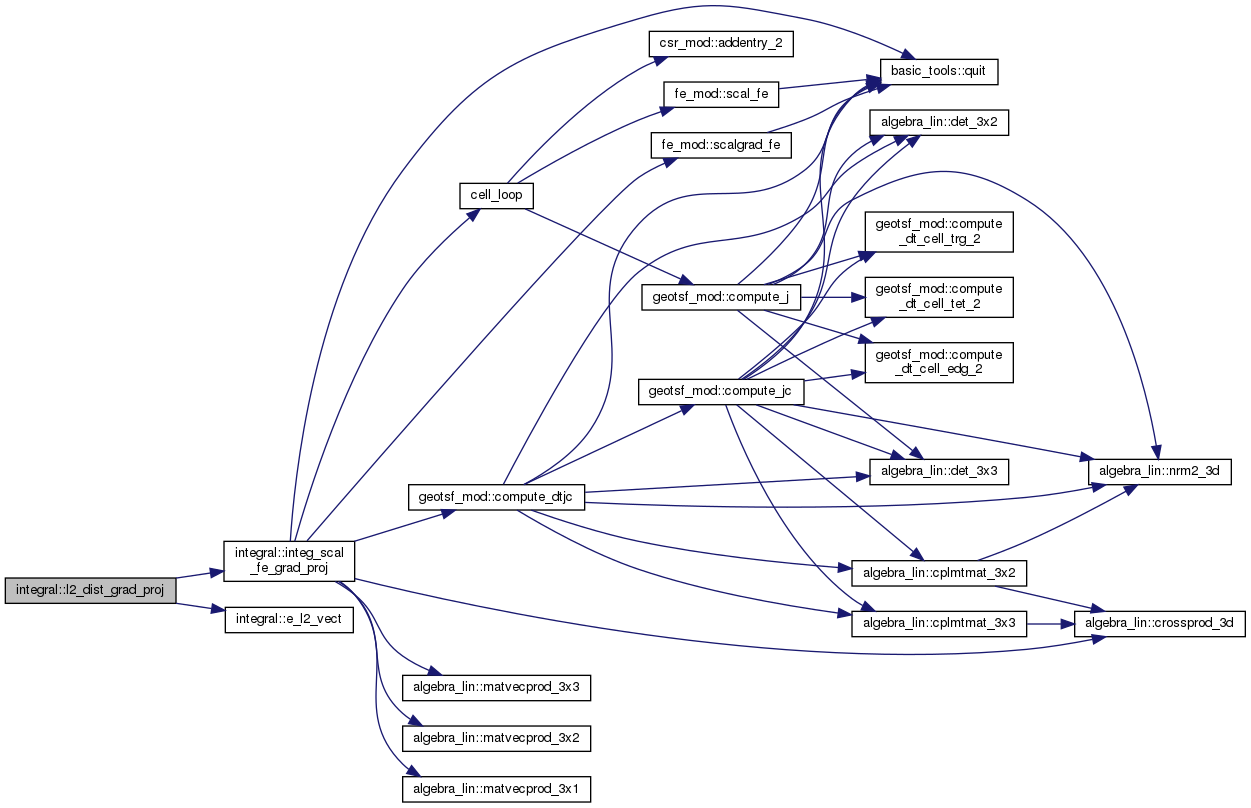
◆ l2_dist_grad_scalfe()
|
private |
Returns \( \int_O \vert \phi - \nabla u_h \vert^2 \dx \).
- \(\phi~: \R^3 \mapsto \R^3 \) is a vector function,
- \( u_h~: \Omega \mapsto \R\) is a scalar finite element function in the finite element space \( X_h \)
(associated to a mesh \( \T \) with domain \( \Omega \)),
- 'qdm' = integration method on the mesh \( \T \),
- \( O \) is the integration domain, see quadmesh_mod for a definition.
Definition at line 934 of file integral.F90.
◆ l2_dist_scalfe()
|
private |
Returns \( \int_O \vert u - u_h \vert^2 \dx \).
- \( u~: \R^3 \mapsto \R \) is a scalar function,
- \( u_h~: \Omega \mapsto \R\) is a scalar finite element function in the finite element space \( X_h \)
(associated to a mesh \( \T \) with domain \( \Omega \)),
- 'qdm' = integration method on the mesh \( \T \),
- \( O \) is the integration domain, see quadmesh_mod for a definition.
Definition at line 905 of file integral.F90.
◆ l2_dist_vect()
| real(rp) function, public integral::l2_dist_vect | ( | procedure(r3tor3) | phi, |
| real(rp), dimension(:), intent(in) | phi_h, | ||
| type(fespace), intent(in) | X_h, | ||
| type(quadmesh), intent(in) | qdm | ||
| ) |
Returns \( \int_O \vert \phi - \phi_h \vert^2 \dx \).
- \( \phi~: \R^3 \mapsto \R^3 \) is a vector function,
- \( \phi_h~: \Omega \mapsto \R^3\) is a vector finite element function in the finite element space \( X_h \)
(associated to a mesh \( \T \) with domain \( \Omega \)),
- 'qdm' = integration method on the mesh \( \T \),
- \( O \) is the integration domain, see quadmesh_mod for a definition.
Definition at line 986 of file integral.F90.
 1.8.13
1.8.13